Key Takeaways
- XR technologies are transforming the design and development process in the automotive and mobility industries.
- XR can be used in education and onboarding to drive sales by allowing consumers to experience advanced features in a virtual setting and learn about their new vehicle's capabilities.
- Offering an immersive, informative experience makes consumers knowledgeable and excited about their new vehicle, driving future sales and securing a competitive edge.
- Automotive companies must adopt XR to meet the rising demands of tech-savvy consumers and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
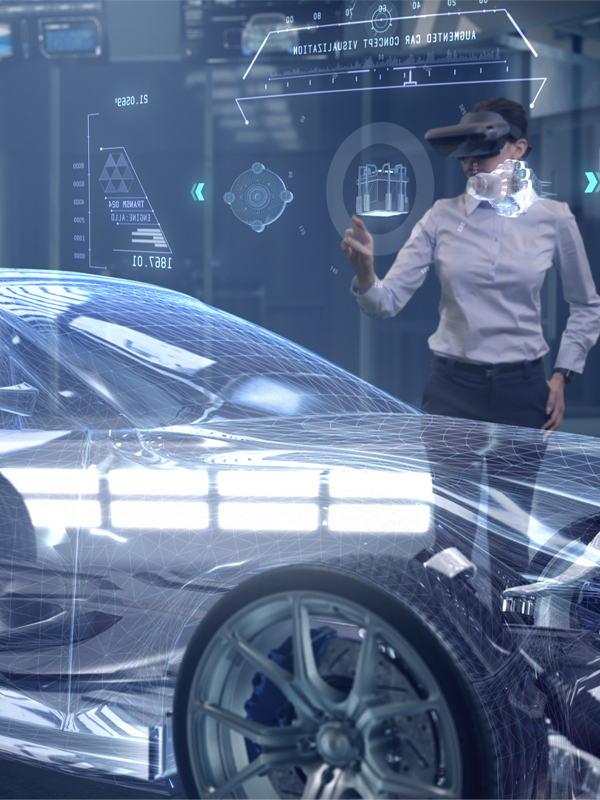
It is not hard to see how extended reality technologies are transforming the design and development process in the automotive and mobility industries. Surely among the biggest motivators for adopting these technologies is reducing cost and time to bring these products to market. But, design and development are only part of a complex chain of processes to bring a car, boat, or plane to the consumer. In manufacturing marketing and sales, there are massive opportunities to innovate using XR.
In this article, we will discuss some ways mobility companies are already using XR and then envision some innovations that could transform the way we educate, onboard, and provide value to an evolving consumer set. The potential for XR reaches into many adjacent industries, starting with aerospace and health sciences.
Early adoption of XR technology in the aerospace industry
The aerospace industry was among the first to adopt advanced technologies like real-time 3D simulators, extended reality, and advanced CAD / CAM systems for design and manufacturing. Training simulators were first seen in military and aerospace applications. High-risk operations like space missions to the moon or putting humans into orbit provide some of the best use cases for immersive simulations.
I served at NASA Ames Research Center, designing simulators to prepare astronauts for docking the space shuttle with the International Space Station. These simulations were high stakes, testing the astronauts' skills through each maneuver. Any critical mistake served as a stark reminder of the dangers involved in space flight.
By integrating precise physics models with high-fidelity 3D environments, developers created a realistic docking simulator that places astronauts right in the pilot's seat. Subsequent research focused on how intelligent assistant systems could compensate for pilot errors during critical maneuvers. This innovative approach has since been adopted in commercial aviation, requiring pilots to train on state-of-the-art simulators to achieve their flight certifications. The early pioneering efforts in aerospace have paved the way for the advanced technologies we now witness in the mobility sector.
Simulation and virtual training
Tele-immersive simulations allow companies like BMW to design and train employees on manufacturing processes. Since 2014, BMW has led the charge in digitalization, innovating in design, manufacturing, and sales to enhance efficiency across its vehicle operations.
Among other things, BMW has developed VR workstation training, a mixed reality platform for simulated drive experiences, and AR training for engine assembly and other processes. Recently, BMW partnered with Nvidia to develop its inaugural virtual factory, utilizing Nvidia’s Omniverse to create an intricate digital twin. This groundbreaking digital twin allows planners to meticulously design, collaborate, and simulate configurations for every aspect of a factory planned to launch in 2025.
But what is the real advantage of this type of virtual factory? One clear advantage is the ability to visualize every facet of factory operations in real time. However, a more crucial benefit is the capacity for remote teams to experiment with new designs or processes in virtual reality, under the observation of an engineer from afar.
For example, they can test ergonomic configurations for tool carts and workstations with someone in virtual reality and have an engineer modify the configurations in real time. Once a factory's design is complete, the digital twin can also be used to train people on assembly line procedures, safety protocols, and so on. What we are starting to see is the emergence of tele-immersive design and simulation across international business units.
Virtual showrooms
The way we market and sell cars is also changing. Customer’s preferences for how they interact with goods and services have undergone a massive transformation with the advent of digital technologies like smartphones. And since the pandemic, we have witnessed a huge shift in consumers buying preferences and behaviors—most notably, the shift to buying goods online. At the forefront of adopting immersive tech as part of their showroom experience is Lucid Motors.
A modern and innovative EV brand needed an equally innovative car-buying experience. One that made selecting a new car not just about colors and trim levels but an immersive journey that put the consumer behind the wheel. The solution was to combine an online configurator with a new kind of showroom they call a “Lucid Studio Showroom.” The path to purchase is personalized and designed for the forward-thinking luxury EV buyer by seamlessly bridging the virtual and physical worlds.
Instead of having many vehicles in the showroom, customers can bring their configurator code into the studio and step into a VR experience that Lucid Motors calls “edutainment.” Sitting in a two-seater cockpit, customers don a headset and are able to test new car features, take a drive in Big Sur, or further customize the car they would like to purchase. Customers can, of course, drive the physical car, but isn't it great if the first time you drive a Lucid Air, you already know and have tried all the features of these futuristic cars? Virtual showrooms are becoming part of the customer journey, and XR is opening new possibilities for the car-selling experience.
Using XR in education and onboarding to drive sales

The age of digitalization means that no process in the production of a vehicle should remain in a silo of its own. A feedback loop can be established that knits sales and marketing to the design and development process. Digital technologies can help us understand the behaviors and preferences of our customers by purposefully implementing technologies that create feedback loops between design and development, education and onboarding, and marketing and sales. Data is the backbone of all processes. How then do we use spatial computing in education and onboarding to drive sales and key insights for engineers and designers?
Educating consumers on advanced features
Beyond the ability to configure and customize vehicles, XR technologies offer consumers the opportunity to learn about and experience advanced features in a safe and controlled environment. Imagine a prospective buyer testing out autonomous cruise control or lane change on demand through an immersive simulation before even setting foot in a real car. These advanced features, which might seem daunting or complicated when explained through traditional means, can be intuitively understood and appreciated when experienced firsthand in a virtual setting. This not only enhances the consumer's knowledge but also builds their confidence in using these features, ultimately leading to a more satisfying ownership experience.
Onboarding new car owners
The onboarding process in an immersive environment can also significantly reduce the learning curve for new car owners. By interacting with a virtual version of the car, customers can explore and master various functions and features at their own pace. For instance, they can learn how to adjust settings, use infotainment systems, and even perform basic maintenance tasks, all within a risk-free virtual space. This level of engagement and education is unparalleled, providing consumers with a deep understanding of their vehicle's capabilities and fostering a stronger connection to the brand.
Meeting the rising demands of consumers
As industries evolve, the adoption of these immersive technologies is becoming increasingly vital. Automotive companies can look to adjacent industries, such as aerospace and health care, which have long utilized XR for training and simulation purposes. By integrating XR into the car buying journey, automotive brands can not only meet the rising expectations of today's tech-savvy consumers but also position themselves at the forefront of innovation. The power to provide a comprehensive, immersive, and educational experience is paramount, ensuring that consumers are not only informed but also excited about their new vehicle. This approach will be key to driving future sales and maintaining a competitive edge in the ever-evolving automotive market.






